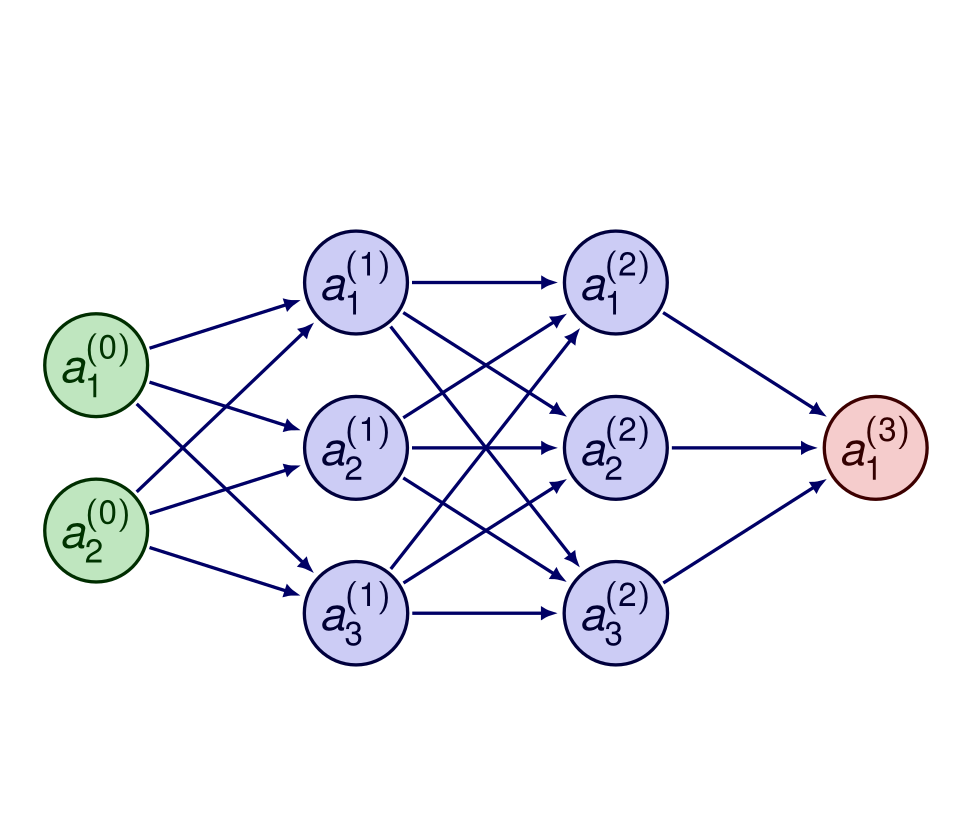
Turbulence modeling using Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a method whjich originally was used for teaching the algorithm to classify another
set of data.
- Photographs where the machine learning algorithm should recognize,
e.g., traffic lights
- CG signals
where the machine learning algorithm should recognize certain unhealthy conditions of the heart
- Detecting fraud for credit card payments
Machine learning methods such as
Support Vector Machines (SVM) and neural networks (NN) are used for solving this type of problems.
In turbulence modeling, input and output
are numerical values. Regression methods (SVR or NN) should be used; in the course, the participants will learn to
use
Neural Network and Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN). Day 3, we will also look at binary search trees (KDTree)
for improving wall functions. The students will be given simple Python scripts (PyTorch) for NN, PINN and KDTree.
The NN and PINN models will be exported to disk and the participants will import and use these models in simple RANS codes,
either →RANS.py or
→pyCALC-RANS.py.
The participants can also use their
own in-house CFD codes (if it's possible to import Pyuthon modules).
Note that
all Python scripts used in course (CFD codes, NN, PINN, KDTree scripts) are written by the lecturer.
Good YouTube lectures on NN are found at the links below:

THE ON-LINE COURSE
The course includes lectures (9 hours) and workshops (12 hours). The
course is given 29 June, 1, 3, July 2026.
The lectures will be given on-line (Live) using →Zoom. During the workshops, the participants will get
supervision in a joint Zoom room which will enable participants to learn from each others questions. Part of the supervision
may also be given in individual break-out Zoom rooms.
 →Zoom →Zoom

OBJECT
The participants will be given an introduction to Neural Network (NN) and Physics-Informed NN.
The object is not that the participants should understand all the details of NN but that they should learn how to use
it for improving and/or creating turbulence models. This understanding is applicable to all modelling in engineering physics.
The objective is that the participants should learn the importance to choose and test different input and output parameters
based on the physical problem.
For instance, the lecturer is currently trying to improve the wake model in
→Floris used for predicting and controling wind farms.
The key thing is to understand the physical problem and the equations -- often partial differential
equations -- not the details of the NN.

PARTiCiPANTS
The participants are expected to hold a MSC degree or PhD degree related to fluid mechanics. They are expected
to have at least a basic knowledge in turbulence models. Programming skills in Pythons is highly recommended.

LECTURER
The lecturer at the course (both during lectures and workshops) will be →Prof. Lars Davidson,
Chalmers University of Technology.
 →homepage →homepage

COURSE MATERiAL

COURSE LANGUAGE
The course material is in English and the lectures will be given in English.

DATE & LOCATiON
The course will be held 1, 3, 5 July 2026 online at →Zoom

REGiSTRATiON
Registration form should be submitted no later than June 6, 2026.
The price is 14,700 SEK (excl. VAT). No refunding after June 6.
The number of participants is limited to 16.
 registration form registration form

PRELIMINARY PROGRAM
The course will include three lectures (45 minutes) and four workshops (45 minures) every day.
The time when the first lecture starts will be determined so that it fits all participants as well as possible. This
time will be set when the invoices are sent to the participants.
DAY 1, Monday, 7 hours
Tueday (no teaching). Participants can work on using the RANS codes
DAY 2, Wednesday, 7 hours
- Lecure 1: introduction to NN
- Workshop 1, 2: use a simple NN model to compute damping functions in a k-eps model
- Lecure 2: how to use NN for predicting multiple output paramters (e.g. many coefficients in a non-linear k-eos models)
- Workshop 3: use a NN model to compute damping functions in a k-eps model
- Lecure 3: how to use NN for improving an Explicit Algebraic Reynolds Stress Model (EARSM)
- Workshop 4: use a NN model to imrprove an EARSM. Which input parameters (y+, P_k, nu_t ...) can be used?
Thursday (no teaching). Participants can work on NN models
DAY 3, Friday, 7 hours
- Lecure 1: introduction to PINN
- Workshop 1, 2: use PINN to solve implicit one-dimensional ODE:s (e.g. solve for the diffuion coefficient)
- Lecure 2: How to use PINN in two dimensions
- Workshop 3: use PINN to solve implicit two-dimensional ODE:s
- Lecure 3: How to use binary search trees for improving turbulence models
- Workshop 4: use KDTree to create new wall functions

QUESTiONS & FURTHER iNFORMATiON
Please contact
- →Lars Davidson
- tel. +46 (0) 730-791 161
- E-mail: lada@flowsim.se, lada@chalmers.se

REFERENCES
- P. Emvin, The Full Multigrid Method Applied to Turbulent Flow in Ventilated
Enclosures Using Structured and Unstructured Grids. PhD thesis, Dept. of
Thermo and Fluid Dynamics, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg,
1997.
- L. Davidson, Large eddy simulations: how to evaluate resolution. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 30(5):1016-1025, 2009.
- L. Davidson, The PANS k-ε model in a zonal hybrid RANS-LES formulation. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 46:112-126, 2014.
- L. Davidson, Zonal PANS: evaluation of different treatments of the RANS-LES interface. Journal of Turbulence, 17(3):274-307, 2016.
- A. Altintas and L. Davidson, Direct numerical simulation analysis of spanwise oscillating lorentz force in turbulent channel flow at low Reynolds number. Acta Mechanica, pages 1-18, 2016.
- J. Ma, S.-H. Peng, L. Davidson, and F. Wang, A low Reynolds number variant of Partially-Averaged Navier-Stokes model for turbulence. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 32(3):652-669, 2011.10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2011.02.001.
- L. Davidson, Using isotropic synthetic fluctuations as inlet boundary conditions for unsteady simulations. Advances and Applications in Fluid Mechanics, 1(1):1-35, 2007.
- L. Davidson and S.-H. Peng, Embedded large-eddy simulation using the partially averaged Navier-Stokes model. AIAA Journal, 51(5):1066-1079, 2013.
- L. Davidson, Two-equation hybrid RANS-LES models: A novel way to treat k and ω at inlets and at embedded interfaces. Journal of Turbulence, 18(4):291-315, 2017.
- B. Nebenfuhr, L. Davidson, Large-Eddy Simulation Study of Thermally Stratified Canopy Flow, Boundary-Layer Meteorology, Vol. 156, number 2 , pp. 253-276, 2015
- B. Nebenfuhr, L. Davidson, Prediction of wind-turbine fatigue loads in forest regions based on turbulent LES inflow fields, Volume 20, Issue 6 pp. 1003-1015, Wind Energy, 2017.
- L. Davidson and C. Friess,
The PANS and PITM model: a new formulation of f_k,
Proceedings of 12th International ERCOFTAC Symposium on Engineering Turbulence Modelling and Measurements (ETMM12), Montpelier,
France 26-28 September, 2018
- L. Davidson, Zonal Detached Eddy Simulation coupled with steady RANS in the wall region,
ECCOMAS MSF 2019 Thematic Conference, 18-20 September 2019, Sarajevo, Bosnia-Herzegovina
- L. Davidson, →inlet boundary conditions.
- L. Davidson, "Non-Zonal Detached Eddy Simulation coupled with a steady RANS solver in the wall region",
ERCOFTAC Bullentin 120, Special Issue on Current trends in
RANS-based scale-resolving simulation methods, pp 43-48, 2019.
- L.M. Olson abd J.B. Schroder, PyAMG: Algebraic Multigrid Solvers in Python,
Release 4.0, 2018
-
L. Davidson and Ch. Friess, "Detached Eddy Simulations: Analysis of a limit on the dissipation term for reducing spectral
energy transfer at cut-off",
ETMM13: The 13th International ERCOFTAC symposium on engineering, turbulence, modelling
Rhodes, Greece, 15-17 September, 2021
→View PDF file
-
L. Davidson
"Detached Eddy Simulation coupled with steady RANS in the wall region",
ETMM13: The 13th International ERCOFTAC symposium on engineering, turbulence, modelling
Rhodes, Greece, 15-17 September, 2021
→View PDF file
-
L. Davidson,
"Non-Zonal Detached Eddy Simulation coupled with a steady RANS solver in the wall region",
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, Vol.92, 108880, 2021
→Get article at publisher
-
L. Davidson
"Using Machine Learning for formulating new wall functions for Large Eddy Simulation: A First Attempt",
Div. of Fluid Dynamics, Mechanics and Maritime Sciences,
Chalmers University of Technology, 2022.
→View PDF file
-
L. Davidson
"Using Machine Learning for formulating new wall functions for Large Eddy Simulation: A Second Attempt",
Div. of Fluid Dynamics, Mechanics and Maritime Sciences,
Chalmers University of Technology, 2022.
→View PDF file
-
L. Davidson
"pyCALC-LES: A Python Code for DNS, LES and Hybrid LES-RANS"
Div. of Fluid Dynamics, Mechanics and Maritime Sciences,
Chalmers University of Technology, 2022.
→Download pyCALC-LES
-
L. Davidson
"Using Machine Learning for formulating new wall functions for Detached Eddy Simulation",
ERCOFTAC symposium on Engineering, Turbulence, Modelling and Measurements (ETMM14),
in Mini-Symposium: Machine learning for turbulence, Barcelona, Spain 6th - 8th September 2023;
Chalmers University of Technology, 2022.
→View PDF file
-
L. Davidson
"Using Machine Learning for Improving a Non-Linear k-eps Model: A First Attempt",
Div. of Fluid Dynamics, Mechanics and Maritime Sciences,
Chalmers University of Technology, 2023.
→View PDF file
-
L. Davidson
"Using Neural Network for Improving an Explicit Algebraic Stress Model in 2D Flow",
CUSF 2024, Proceedings of the Cambridge Unsteady Flow Symposium",
Springer, Editors: J. C. Tyacke and N. R. Vadlamani, 2024 (to appear)
→View presentation
→View PDF file
→Proceedings
→Download code
-
L. Davidson
"Hybrid LES/RANS for flows including separation: A new wall function using Machine Learning based on binary search trees",
Journal of Turbulence, 2025.
→Get article at publisher
→Download Python script and databases
-
L. Davidson
"Using Physical Informed Neural Network (PINN) to Improve a k-omega Turbulence Model",
ERCOFTAC Symposium on Engineering Turbulence Modelling and Measurements (ETMM-15),
Dubrovnik on 22-24 September 2025.
→Download Python script and databases
-
L. Davidson
"Using Physics Informed Neural Network (PINN) and Neural Network (NN) to Improve a k-omega Turbulence Model",
→Get article at arXiv
→Download paper, Python scripts and CFD codes
-
L. Davidson
"Understanding Autograd and Neural Network in PyTorch",
Div. of Fluid Dynamics, Mechanics and Maritime Sciences,
Chalmers University of Technology, 2025.
Download paper


|